Optimizing Cerebral Bypass Surgery with Augmented Reality
Neurosurgery
Project Team:
Last Updated: 11/13/2024
Short Description
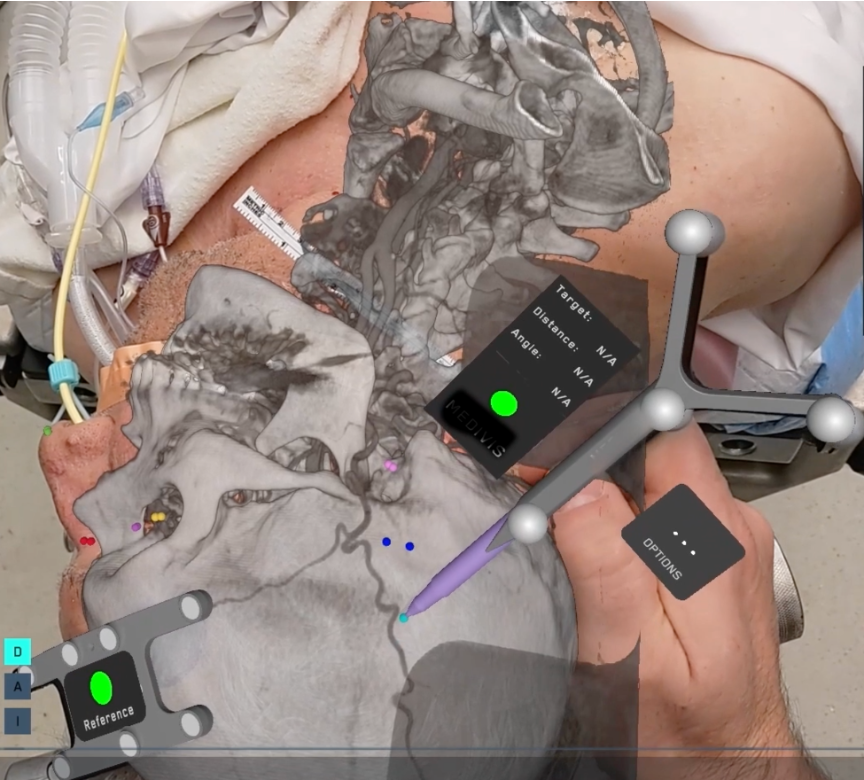
Using AR to optimize the pre-operative workflow for STA-MCA bypass surgery
Full Description
Moyamoya is a rare intracranial vascular disease that commonly requires an extracranial-intracranial (EC-IC) bypass surgery to reestablish flow to ischemic areas of the brain. In this surgery, an anastomosis is created between the superficial temporal artery (STA) to the middle cerebral artery (MCA). In the pre-operative setting, accurate mapping the STA is a critical factor for a successful surgery. The current gold standard for mapping the STA is conducted using a Doppler imaging probe; however, there are several shortcomings with this technology. This process is often time-consuming and is imperfect because it does not approximate the course of the STA accurately. Additionally, the size of the incision can be larger and can unnecessarily prolong the surgery. The implementation of a real-time augmented reality (AR) system can help overcome these limitations. By overlaying the target vessel onto the surgical field before the skin incision is made, surgeons can trace and anticipate the location of the STA faster and with more accuracy.
This study is the first to offer a comparative analysis of mapping the STA conducted with and without AR. Preliminary data has shown that AR-guided mapping is significantly faster and more efficient than traditional Doppler-guided mapping of the STA. This data is crucial for establishing standardized clinical outcomes related to the use of AR in neurosurgery and may pave the way for broader application in other surgical disciplines.